The Importance of Nonmagnetic Tools in Health & Medical Practices
In the ever-evolving landscape of health and medical services, particularly in sectors like Medical Centers and Diagnostic Services, the use of specialized tools is paramount. One category of tools that has gained significant attention is nonmagnetic tools. These instruments are crucial for ensuring patient safety, improving diagnostic accuracy, and enhancing treatment effectiveness. As we delve into the importance of nonmagnetic tools, we will also explore their applications, benefits, and the technology behind them.
Understanding Nonmagnetic Tools
Nonmagnetic tools are instruments that do not respond to magnetic fields. They are typically engineered from materials such as titanium, plastic, or certain types of stainless steel that do not contain ferromagnetic properties. This characteristic makes them indispensable in various medical contexts, particularly when magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is involved.
Why Nonmagnetic Tools Matter in Medical Settings
In the realm of health and medical practices, safety and precision are critical. The incorporation of nonmagnetic tools helps mitigate risks associated with magnetism, especially in settings that utilize MRI technologies. Here are some compelling reasons that highlight the importance of these tools:
- Patient Safety: The foremost benefit of using nonmagnetic tools lies in patient safety. Ferromagnetic tools can pose serious risks during MRI procedures, potentially causing injury or machinery malfunction.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Nonmagnetic materials do not distort imaging results, thereby aiding in precise diagnostics. They enable healthcare professionals to obtain clearer images and perform accurate assessments.
- Versatility: Nonmagnetic tools can be utilized across various medical fields - from surgery to rehabilitation - providing flexibility in their applications.
- Enhanced Workflow: Their lightweight characteristics and resistance to magnetic interference streamline workflows in hospitals and clinics.
Applications of Nonmagnetic Tools in Healthcare
The application of nonmagnetic tools spans a wide range of medical practices. Here are some key areas where these tools make a significant impact:
1. Diagnostic Imaging
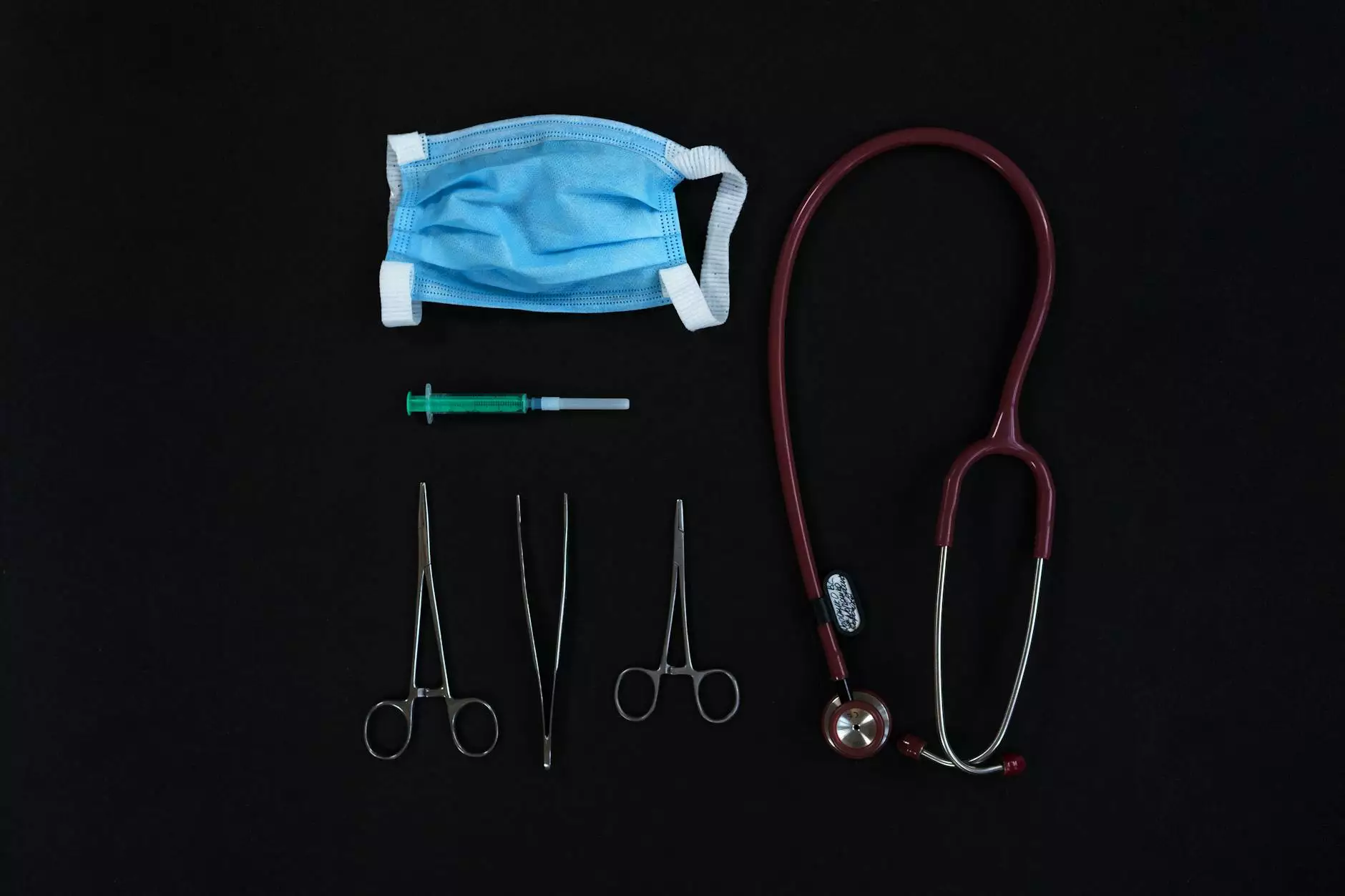
In diagnostic imaging, particularly when working with MRI machines, the use of nonmagnetic tools is essential. Tools such as nonmagnetic scalpels, forceps, and other surgical instruments are necessary to avoid interference with the magnetic field. This ensures that the imaging remains clear and that the patient's safety is never compromised.
2. Surgical Procedures
During surgical procedures, it's vital for instruments to be nonmagnetic, especially if the procedure is occurring in proximity to MRI machines or other magnetic devices. Utilizing nonmagnetic tools like clamps, scissors, and retractors minimizes risks and maximizes operational efficiency.
3. Rehabilitation Services
In rehabilitation therapy, nonmagnetic tools are often employed in physical therapy settings, especially those that incorporate devices like magnetic coils for stimulation purposes. Here, the use of nonmagnetic equipment ensures that there is no disruption in the therapeutic processes.
4. Emergency Care
In an emergency room setting, having nonmagnetic emergency tools ensures that healthcare providers can act swiftly and effectively without the risk of equipment failing due to magnetic interference. Instruments such as splints, bandages, and even some imaging devices must be nonmagnetic to maintain efficacy.
Benefits of Using Nonmagnetic Tools
The benefits of integrating nonmagnetic tools into medical practice are numerous, providing both immediate and long-term advantages:
- Reduced Risk of Accidents: Nonmagnetic tools minimize workplace hazards, reducing patient and staff injuries associated with magnetic accidents.
- Increased Confidence: Healthcare professionals can operate with greater confidence knowing that their tools are safe for use in sensitive environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Though initial investment may be slightly higher, the long-term benefits in terms of patient safety and diagnostic efficiency outweigh these costs.
- Durability: Many nonmagnetic materials are designed to withstand repeated use and sterilization processes, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Choosing the Right Nonmagnetic Tools
When selecting nonmagnetic tools, medical facilities must consider various factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability:
1. Material Quality
The integrity of the materials used to manufacture nonmagnetic tools is crucial. High-quality titanium or specialty stainless steels offer enhanced durability and are essential for regular usage in medical settings.
2. Design Ergonomics
Tools should be ergonomically designed for comfort and efficiency. Healthcare professionals often handle these tools for extended periods, making the design aspects critical to reducing fatigue and improving precision.
3. Compliance with Health Standards
All medical tools, including nonmagnetic tools, should comply with industry standards and regulations. This compliance guarantees that the tools meet health and safety requirements, ensuring the well-being of both patients and healthcare providers.
4. Proven Performance History
Choosing nonmagnetic tools with proven performance records can help medical facilities maintain high standards in patient care. Tools should be backed by research and clinical trials that highlight their effectiveness and safety.
Future Trends in Nonmagnetic Tool Development
The technology surrounding nonmagnetic tools is continually evolving, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
- Smart Tool Integration: Future developments may include smart technology, allowing tools to communicate with diagnostic machines for real-time data sharing and enhanced patient outcomes.
- Bio-Compatible Materials: Innovations will likely focus on using materials that not only are nonmagnetic but also exhibit biocompatibility, reducing the risk of allergic reactions.
- Customizable Tools: The ability to customize tools for specific surgical or diagnostic procedures is becoming more accessible, allowing for surgical instruments that fit unique requirements.
- 3D Printing Technology: The integration of 3D printing in tool production can lead to increased accessibility and tailored design features that enhance surgical outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of nonmagnetic tools in health and medical practices cannot be overstated. Their importance lies in their ability to enhance patient safety, diagnostic accuracy, and overall operational efficiency in medical centers and diagnostic services. As healthcare technology continues to advance, the demand for high-quality nonmagnetic tools will only increase, solidifying their position as essential components in modern medical practices. By investing in these tools, healthcare providers not only improve the quality of care they deliver but also contribute to the evolution of the medical field, paving the way for safer and more effective healthcare solutions.
For more information on nonmagnetic tools and their applications in healthcare, visit echomagnetservices.com.